Disclaimer: This article is meant purely for educational purposes and public interest. The information is based on official documents, trade reports, and government publications related to the India–Korea Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA). We do not claim ownership of any official content. Trade agreements and duty structures are subject to change; always consult DGFT notifications, CBIC circulars, or ICEGATE service centres for the latest updates before filing or claiming CEPA benefits.
Introduction
Did you know that over 70% of India’s imports from South Korea qualify for lower customs duties because of CEPA?
The India–Korea Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) is one of the most impactful trade deals India has signed in the last two decades. It has reshaped trade flows between the two countries, making it easier — and often cheaper — for Indian businesses to import machinery, steel, electronics, and other Korean products.
But here’s the catch: while CEPA reduces costs for importers, it also raises concerns about domestic industries struggling to compete with Korean goods.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover:
What CEPA is and how it works
Advantages and disadvantages of importing from Korea under CEPA
Preferential duty rates by product chapters (with real examples)
How businesses can claim CEPA benefits step-by-step
Mistakes to avoid and FAQs every importer should know
By the end, you’ll have a complete understanding of CEPA from an importer’s perspective — whether you’re in steel, electronics, auto parts, or chemicals.
What is the India–Korea Free Trade Agreement (CEPA)?
The India–Korea CEPA, signed in 2009 and operational since January 2010, is a bilateral trade agreement that goes beyond a traditional Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
Here’s why it matters:
It allows preferential tariff reductions (lower customs duties) on thousands of products traded between India and South Korea.
Unlike a standard FTA, CEPA also includes services, investment, and intellectual property rights, making it a more comprehensive pact.
Over the years, both countries have expanded the agreement, reducing duties on more products and revising schedules.
In simple terms:
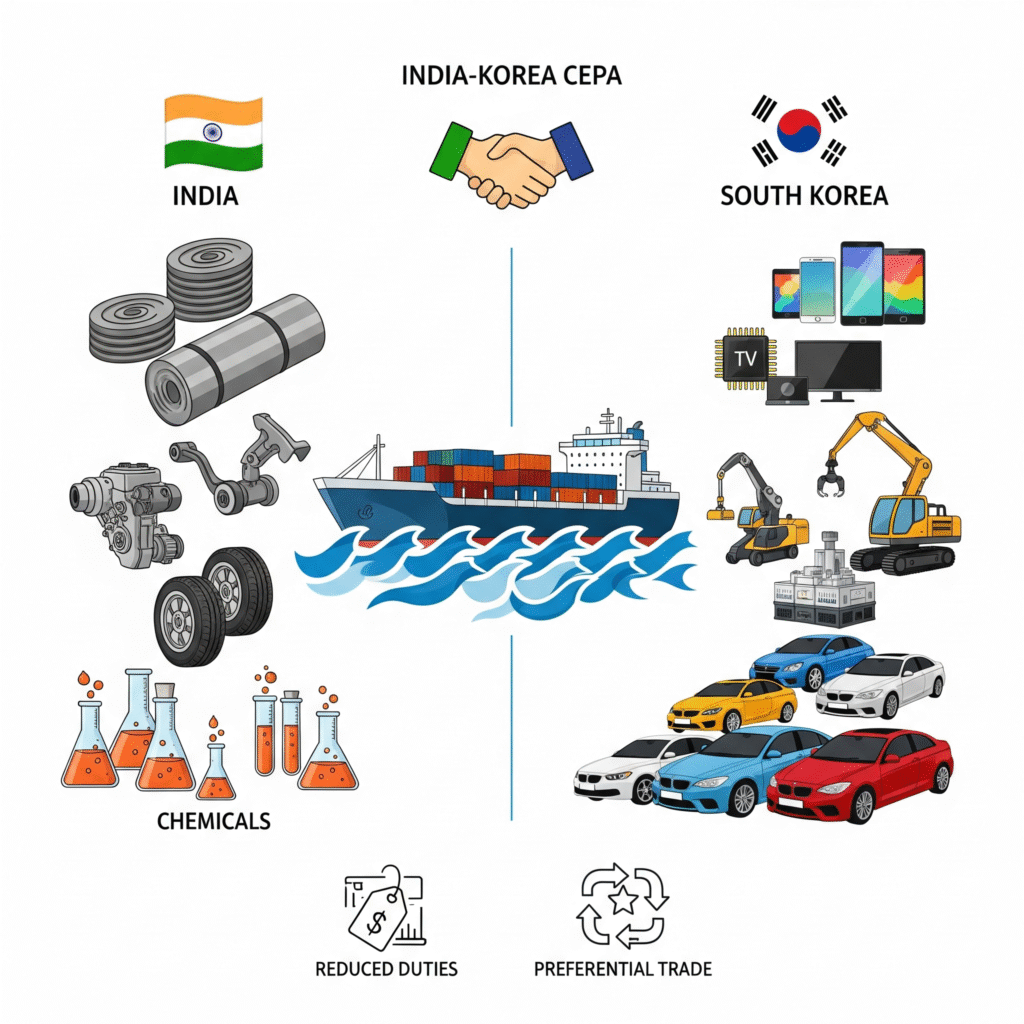
If you are importing machinery, chemicals, steel, or electronics from Korea, CEPA can help you save significantly on customs duty, provided your goods fall under the preferential duty schedule.
For background, you can also check our complete import-export and customs clearance process in India.
How Does CEPA Work for Indian Importers?
When an Indian importer brings goods from South Korea, the normal customs duty (MFN – Most Favoured Nation rate) applies. But under CEPA, if the product is listed in the preferential tariff schedule, the importer can pay a reduced duty rate (sometimes even zero).
To claim this benefit, the importer must:
Check the HS Code of the product (Chapter/Subchapter listed in CEPA schedule).
Verify preferential duty rate under CEPA for that HS code.
Ensure the goods are of Korean origin (supported by a Certificate of Origin issued by Korean authorities).
Declare CEPA claim at the time of filing the Bill of Entry in India.
This way, businesses can legally reduce import costs and gain a competitive advantage in pricing.
Advantages of Importing from South Korea Under CEPA
South Korea is known for its cutting-edge technology, advanced manufacturing, and high-quality exports. CEPA makes it more affordable for Indian businesses to access these.
1. Lower Customs Duties = Reduced Costs
Many Korean goods attract 0–5% customs duty instead of the higher standard duty (10–20% or more).
For example, automobile parts that usually attract 10% duty may come in at 5% or even duty-free under CEPA.
(Also read: Customs Duty FAQs for clarity on how duties are applied.)
2. Access to High-Quality Products
Korea is a leader in electronics, machinery, steel, petrochemicals, and automobiles.
Indian industries benefit from reliable, top-quality inputs at competitive prices.
3. Boost for Indian Manufacturing & SMEs
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) can source raw materials, components, and machinery from Korea at lower prices, improving efficiency and profitability.
4. Diversification of Import Sources
Instead of relying heavily on China or Western markets, CEPA gives India an alternate supply partner in East Asia.
This reduces risks tied to overdependence on one country.
For similar regional insights, read about the India–Bangladesh trade dynamics.
5. Growth in Strategic Sectors
Industries like steel, chemicals, auto components, shipbuilding, and IT hardware get a strong boost.
Korean technology collaborations also support Make in India initiatives.
Disadvantages & Challenges of CEPA for Indian Importers
While CEPA brings many benefits, it also has downsides and concerns that importers and policymakers need to watch.
1. Trade Imbalance
India’s imports from Korea have grown much faster than exports to Korea.
This leads to a widening trade deficit, where India buys far more than it sells.
(See how similar imbalances play out in India–US trade deal updates).
2. Pressure on Domestic Industries
Cheap Korean imports (like steel, petrochemicals, and electronics) often undercut Indian producers, hurting local industries.
Small manufacturers may struggle to compete on price.
3. Complex Compliance
To claim CEPA benefits, importers must ensure proper documentation and origin proof.
Any mismatch in HS code classification or missing Certificate of Origin can lead to denial of benefits.
4. Limited Awareness Among Businesses
Many Indian SMEs don’t fully understand CEPA benefits and end up paying higher MFN duties unnecessarily.
5. Risk of Overdependence
Heavy reliance on Korea for critical goods (like auto parts or electronics) may create supply chain vulnerabilities.
 See also:
See also: 


